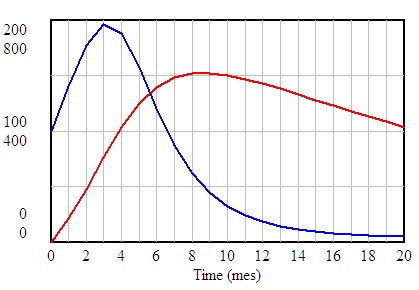
4.20. DEVELOPMENT OF AN EPIDEMIC
A simulation model with Vensim
 Let's imaging a population that is initially healthy, in this population a number people infected with a contagious disease appear. An individual could transmit of catch the illness from other individuals. The transmission of the illness is due to the physical proximity. During the infectious process the individuals can pass through some or all of the following states:
Susceptible (S), the state in which the individual can catch the illness from another infected person.
Let's imaging a population that is initially healthy, in this population a number people infected with a contagious disease appear. An individual could transmit of catch the illness from other individuals. The transmission of the illness is due to the physical proximity. During the infectious process the individuals can pass through some or all of the following states:
Susceptible (S), the state in which the individual can catch the illness from another infected person.
Infected (I), the state in which the individual finds himself infected and can infect others.
Recuperated (R), or cured, the state during which the individual can not infect be infected because he will have acquired an immunity (temporary or permanent) nor can he infect others as he is recuperated or he has passed through the contagious stage of the illness.
In the various infectious diseases, we can find two principle groups:
Those that produce immunity (temporary or permanent) in individuals who have been infected and have since recuperated. The majority of these illnesses are of viral origin (sarampion, varicela, poliomyelitis).
Those that, once recuperated, the individual turns to susceptible immediately. These illnesses are mainly caused by bacterial agents (venereal disease, pest and some forms of meningitis) or protozoos (malaria).
Bearing in mind the different states in the infectious process, the epidemiological models can be divided into three big groups:
SIR: The model susceptible-infected-recuperated, related to illnesses that produce permanent immunity and a typical cycle that includes the three states. This does not mean that all the individuals of the population must pass through these stages, some will not be infected and remain healthy in other words, they will remain in state (S). Others will be immunised artificially by vaccination or another method and will pass directly to state (R) without having been infected.
SIRS: The model susceptible-infected-recuperated-susceptible, the same as the previous model but applicable in cases where the immunity is not permanent and the individual is again susceptible after a certain amount of time, such as the flu.
SIS: The model susceptible-infected-susceptible is used in cases where the illness does not produce immunity, the individual can pass from being infected to being susceptible again skipping the recuperation stage completely.
A model can bear in mind the vital dynamics of the population (births, deaths, migratory movements) depending on the temporal horizon studied, the characteristics of the illness and the population being studied.
|

 See the book
See the book

 See the book
See the book